While apparel companies vary in organizational structure, production models, and management objectives, their core manufacturing processes remain fundamentally consistent. Modern garment production typically involves eight essential stages that ensure quality, efficiency, and market responsiveness.

1. Fashion Design
Most mid-sized and large apparel manufacturers employ in-house designers responsible for creating seasonal collections. Fashion design in industrial production falls into two categories:
- Ready-to-wear design: Based on standardized sizing systems that follow anthropometric data for mass production. Designers must select appropriate fabrics and trims while considering production capabilities, equipment limitations, and technical expertise of workers.
- Contemporary fashion design: Focused on trend-driven creations that respond to fleeting market preferences and runway influences.
*Advanced insight: Many brands now integrate 3D design software like CLO 3D or Browzwear to visualize garments pre-production, reducing sampling costs by up to 50%.*
2. Pattern Making
Once designs are approved, pattern technicians translate them into technical patterns. This process involves:
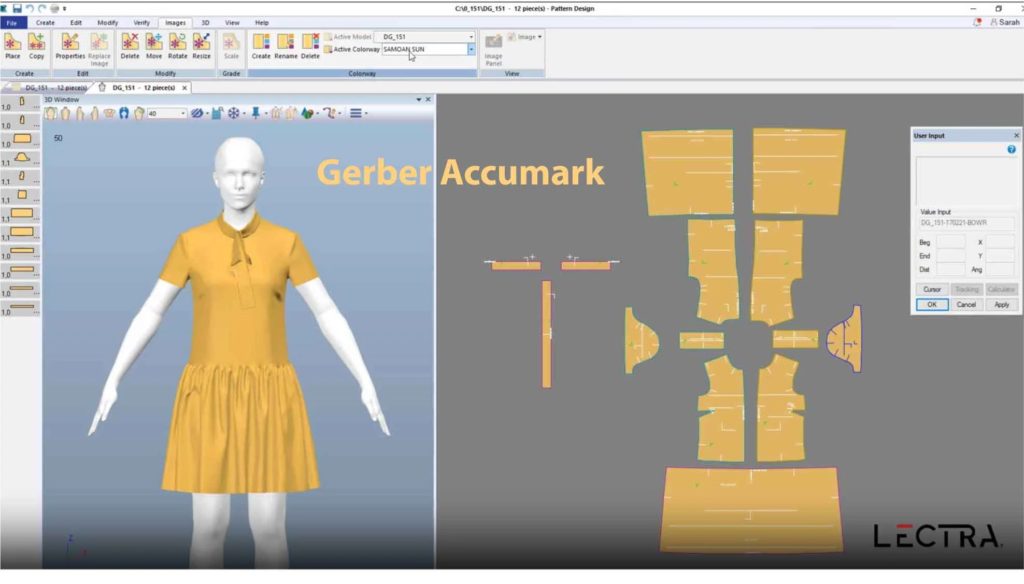
- Grading: Creating size sets through proportional scaling (traditionally done manually, now largely computerized)
- Marker making: Planning fabric cutting layouts to minimize waste—a critical sustainability and cost-control measure
- Digital innovation: AI-powered pattern solutions now automatically generate grading rules and optimize material utilization
3. Pre-Production Preparation
This crucial phase ensures smooth production flow through:
- Material testing: Checking fabric shrinkage, colorfastness, seam strength, and other quality parameters
- Pre-shrinking: Relaxing fabrics to prevent dimensional changes after production
- Sample development: Creating pre-production prototypes for fit confirmation and process planning
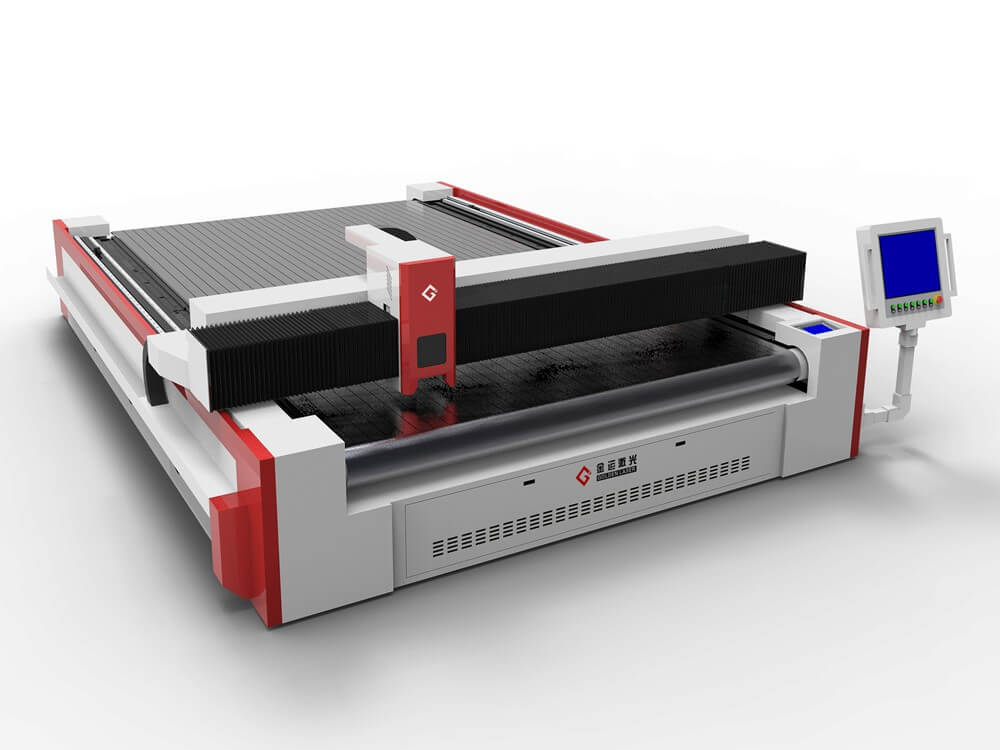
4. Cutting Technology
The first physical production stage involves precision cutting:
- Spreading: Laying fabrics in preparation for cutting, requiring skillful handling of different fabric characteristics
- Cutting methods: Ranging from manual cutting (for small batches) to computerized systems using blades, lasers, or water jets
- Quality control: Including piece inspection, numbering, and bundling to maintain organization throughout production

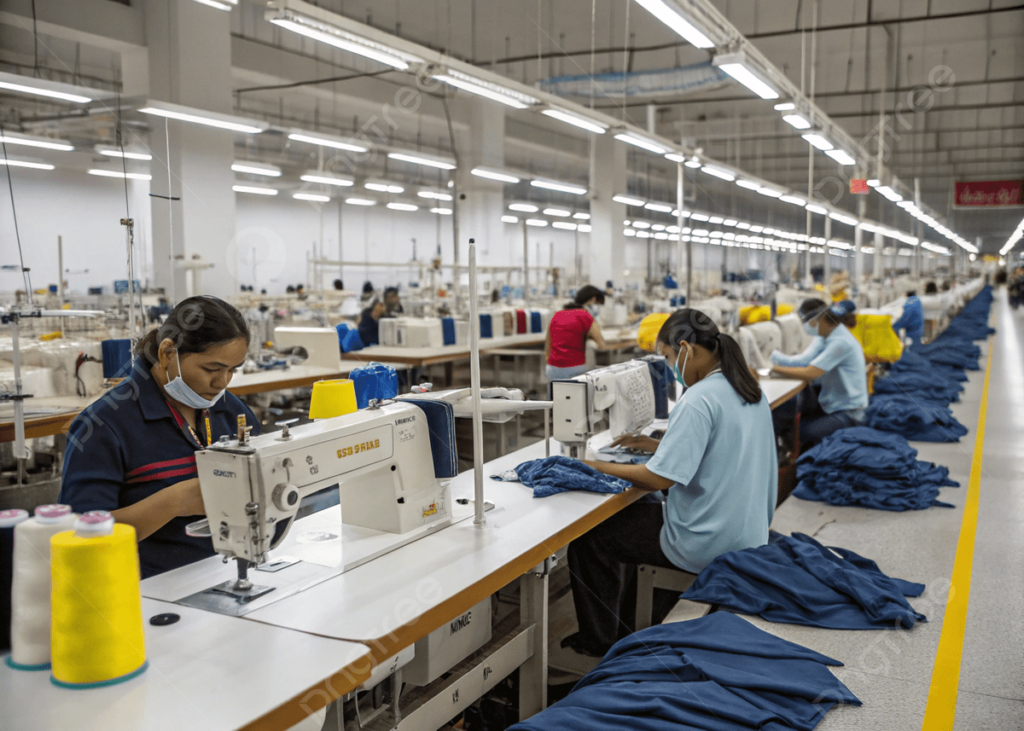
5. Sewing Technology
The most skill-intensive phase where garments take shape:
- Sequence planning: Engineers develop efficient sewing sequences to maximize productivity
- Specialized equipment: Modern factories use automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to move pieces between stations
- Stitch selection: Choosing appropriate stitch types (lockstitch, chainstitch, overlock) based on functional and aesthetic requirements
6. Pressing Technology
Pressing provides the final shape and professional finish:
- Under-pressing: Done during construction for seam setting and shaping
- Final pressing: Critical for achieving the desired silhouette and appearance
- Advanced systems: Modern steam stations with vacuum cooling ensure consistent results while reducing energy consumption
7. Quality Management
Comprehensive quality systems ensure products meet standards:
- In-process inspection: Monitoring at each production stage rather than just final inspection
- Standardized testing: Using instruments like pull testers, color matching cabinets, and wash test machines
- Digital integration: IoT-enabled devices now automatically record quality data for real-time analysis
8. Post-Production Processing
The final stage prepares garments for distribution:
- Sustainable packaging: Growing use of recycled materials and reduced packaging
- RFID tagging: Many brands now embed smart tags for inventory management
- Logistics optimization: Automated sorting systems streamline shipping processes
Industry Evolution: Today’s most advanced factories implement Industry 4.0 principles with connected machines sharing real-time data. This digital transformation enables:
- 30-40% faster production cycles
- 15-20% material waste reduction
- Enhanced customization capabilities
Meta Description:
“Discover the 8 essential steps in modern garment production: from digital design and smart pattern making to automated sewing and quality control. Learn how technology transforms fashion manufacturing.”
SEO Keywords:
garment production process
apparel manufacturing technology
fashion design development
digital pattern making
automated cutting systems
smart sewing technology
quality control in clothing
sustainable apparel manufacturing
Industry 4.0 fashion
apparel production innovation
Summary:
Modern clothing manufacturing combines traditional craftsmanship with digital technology across eight critical processes: design, pattern making, pre-production, cutting, sewing, pressing, quality control, and packaging. Advanced factories now integrate AI, IoT, and automation to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality while maintaining responsiveness to fashion trends.

